Martin Haspelmath
Abteilung für Sprach- und Kulturevolution
Max-Planck-Institut für evolutionäre Anthropologie
Deutscher Platz 6
04103 Leipzig
Telefon: +49 (0) 341 3550 271
E-Mail:
martin_haspelmath@[>>> Please remove the text! <<<]eva.mpg.de
About me
I am a comparative linguist who studies the diversity of the world's grammatical and lexical systems and tries to understand what is universal about them. I am best known for coediting the "World atlas of language structures" (2005/2013), and as a co-founder of "Language Science Press". I am also an honorary (adjunct) professor at Leipzig University.
Curriculum Vitae
| since 2020 | Senior research scientist at DLCE (MPI-EVA) |
| 2015-2020 | Senior research scientist at DLCE (MPI-SHH Jena), ERC project leader at Leipzig University |
| 1998-2015 | Senior research scientist at the Department of Linguistics (MPI-EVA Leipzig) |
| 1994-1996 | Assistant professor, Freie Universität Berlin |
| 1990-1993 | PhD in linguistics, Freie Universität Berlin |
| 1985-1989 | MA in linguistics, University of Cologne and University at Buffalo |
| 1983-1985 | Undergraduate student of linguistics, University of Vienna |
Publications & Presentations
Haspelmath, M. (2021). Explaining grammatical coding asymmetries: Form–frequency correspondences and predictability. Journal of Linguistics, 57(3), 605-633. |
Haspelmath, M. (2020). Human linguisticality and the building blocks of languages. Frontiers in Psychology, 10: 3056. |
Haspelmath, M. (2016). Universals of causative and anticausative verb formation and the spontaneity scale. Lingua Posnaniensis, 58(2), 33-63. |
Dryer, M. S. (2013). The World Atlas of Language Structures Online. München: Max Planck Digital Library. Retrieved from http://wals.info/. |
|
Michaelis, S. M., Maurer, P., Haspelmath, M., & Huber, M. ( |
2025
Haspelmath, M. (2025). Nonverbal clause constructions. Language and Linguistics Compass, 19(2): e70007. |
2024
Haspelmath, M. (2024). Inflection and derivation as traditional comparative concepts. Linguistics, 62(1), 43-77. |
2023
Haspelmath, M. (2023). Coexpression and synexpression patterns across languages: Comparative concepts and possible explanations. Frontiers in Psychology, 14: 1236853. |
|
Skirgård, H., Haynie, H. J., Blasi, D. E., Hammarström, H., Collins, J., Latarche, J. J., Lesage, J., Weber, T., Witzlack-Makarevich, A., Passmore, S., Chira, A.-M., Maurits, L., Dinnage, R., Dunn, M., Reesink, G., Singer, R., Bowern, C., Epps, P., Hill, J., Vesakoski, O., Robbeets, M., Abbas, N. K., Auer, D., Bakker, N. A., Barbos, G., Borges, R. D., Danielsen, S., Dorenbusch, L., Dorn, E., Elliott, J., Falcone, G., Fischer, J., Ghanggo Ate, Y., Gibson, H., Göbel, H.-P., Goodall, J. A., Gruner, V., Harvey, A., Hayes, R., Heer, L., Herrera Miranda, R. E., Hübler, N., Huntington-Rainey, B., Ivani, J. K., Johns, M., Just, E., Kashima, E., Kipf, C., Klingenberg, J. V., König, N., Koti, A., Kowalik, R. G., Krasnoukhova, O., Lindvall, N. L., Lorenzen, M., Lutzenberger, H., Martins, T. R., Mata German, C., van der Meer, S., Montoya Samamé, J., Müller, M., Muradoglu, S., Neely, K., Nickel, J., Norvik, M., Oluoch, C. A., Peacock, J., Pearey, I. O., Peck, N., Petit, S., Pieper, S., Poblete, M., Prestipino, D., Raabe, L., Raja, A., Reimringer, J., Rey, S. C., Rizaew, J., Ruppert, E., Salmon, K., Sammet, J., Schembri, R., Schlabbach, L., Schmidt, F. W., Skilton, A., Smith, W. D., de Sousa, H., Sverredal, K., Valle, D., Vera, J., Voß, J., Witte, T., Wu, H., Yam, S., Ye, J., Yong, M., Yuditha, T., Zariquiey, R., Forkel, R., Evans, N., Levinson, S. C., Haspelmath, M., Greenhill, S. J., Atkinson, Q. D., & Gray, R. D. (2023). Grambank reveals the importance of genealogical constraints on linguistic diversity and highlights the impact of language loss. Science Advances, 9: eadg6175. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2023). Comparing reflexive constructions in the world's languages. In Reflexive constructions in the world's languages (pp. 19-62). Berlin: Language Science Press. |
|
Janic, K., & Haspelmath, M. (2023). Questionnaire on reflexive constructions in the world's languages. In Reflexive constructions in the world's languages (pp. 847-853). Berlin: Language Science Press. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2023). Defining the word. WORD, 69(3), 283-297. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2023). Word-class universals and language-particular analysis. In E. Van Lier ( |
|
Janic, K., Puddu, N., & Haspelmath, M. ( |
2022
Haspelmath, M. (2022). Ergative, absolutive, accusative and nominative as comparative concepts. In L. Iomdin, J. Milićević, & A. Polguère ( |
2021
Haspelmath, M. (2021). Explaining grammatical coding asymmetries: Form–frequency correspondences and predictability. Journal of Linguistics, 57(3), 605-633. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2021). General linguistics must be based on universals (or non-conventional aspects of language). Theoretical Linguistics, 47(1-2), 1-31. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2021). How to tear down the walls that separate linguists: Continuing the quest for clarity about general linguistics. Theoretical Linguistics, 47(1-2), 137-154. |
2020
Haspelmath, M. (2020). The morph as a minimal linguistic form. Morphology, 30(2), 117-134. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2020). Human linguisticality and the building blocks of languages. Frontiers in Psychology, 10: 3056. |
|
Michaelis, S., & Haspelmath, M. (2020). Grammaticalization in Creole languages: Accelerated functionalization and semantic imitation. In W. Bisang, & A. L. Malchukov ( |
2019
Haspelmath, M. (2019). Ergativity and depth of analysis. Rhema, 2019(4), 108-130. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2019). Differential place marking and differential object marking. Language Typology and Universals, 72(3), 313-334. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2019). Can cross-linguistic regularities be explained by constraints on change? In K. Schmidtke-Bode, N. Levshina, S. M. Michaelis, & I. A. Seržant ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2019). Indexing and flagging, and head and dependent marking. Te Reo, 62(1), 93-115. |
2018
Haspelmath, M. (2018). Revisiting the anasynthetic spiral. In H. Narrog, & B. Heine ( |
|
Forkel, R., List, J.-M., Greenhill, S. J., Rzymski, C., Bank, S., Cysouw, M., Hammarström, H., Haspelmath, M., Kaiping, G. A., & Gray, R. D. (2018). Cross-Linguistic Data Formats, advancing data sharing and re-use in comparative linguistics. Scientific Data, 5: 180205. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2018). The last word on polysynthesis: A review article. Linguistic Typology, 22, 307-326. |
2017
Haspelmath, M. (2017). Explaining alienability contrasts in adpossessive constructions: Predictability vs. iconicity. Zeitschrift für Sprachwissenschaft, 36(2), 193-231. |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Karjus, A. (2017). Explaining asymmetries in number marking: Singulatives, pluratives, and usage frequency. Linguistics, 55(6), 1213-1235. |
|
Blasi, D. E., Michaelis, S., & Haspelmath, M. (2017). Grammars are robustly transmitted even during the emergence of Creole languages. Nature Human Behaviour, 1, 723-729. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2017). Some principles for language names. Language Documentation and Conservation, 11, 81-93. Retrieved from http://hdl.handle.net/10125/24725. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2017). An interview on linguistic variation with Martin Haspelmath. Isogloss: A journal on variation of Romance and Iberian languages studies, 3, 99-102. |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Michaelis, S. (2017). Analytic and synthetic: Typological change in varieties of European languages. In I. Buchstaller, & B. Siebenhaar ( |
2016
Haspelmath, M. (2016). Universals of causative and anticausative verb formation and the spontaneity scale. Lingua Posnaniensis, 58(2), 33-63. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2016). The challenge of making language description and comparison mutually beneficial. Linguistic Typology, 20(2), 299-303. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2016). The serial verb construction: Comparative concept and cross-linguistic eneralizations. Language and Linguistics, 17(3), 291-319. |
2015
Comrie, B., Hartmann, I., Haspelmath, M., Malchukov, A., & Wichmann, S. (2015). Introduction. In B. Comrie, & A. Malchukov ( |
|
Grossman, E., & Haspelmath, M. (2015). The Leipzig-Jerusalem transliteration of Coptic. In E. Grossman, M. Haspelmath, & T. S. Richter ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2015). A grammatical overview of Egyptian and Coptic. In E. Grossman, M. Haspelmath, & T. S. Richter ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2015). Descriptive scales versus comparative scales. In I. Bornkessel-Schlesewsky, A. L. Malchukov, & M. D. Richards ( |
|
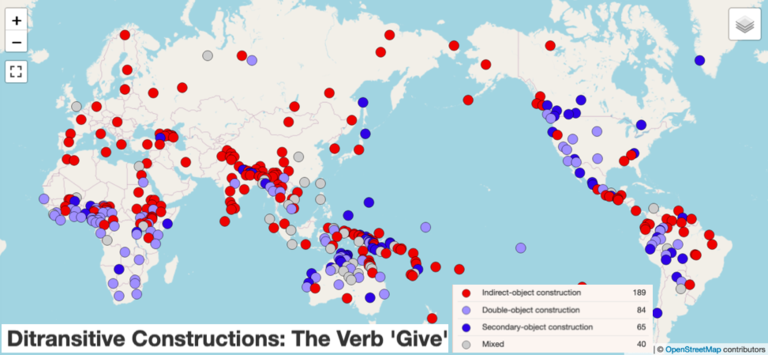
Haspelmath, M. (2015). Ditransitive constructions. Annual Review of Linguistics, 1, 19-41. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2015). The three adnominal possessive constructions in Egyptian-Coptic: Three degrees of grammaticalization. In E. Grossman, M. Haspelmath, & T. S. Richter ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2015). Transitivity prominence. In B. Comrie, & A. Malchukov ( |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Hartmann, I. (2015). Comparing verbal valency across languages. In B. Comrie, & A. Malchukov ( |
|
Haspelmath, M., Grossman, E., & Richter, T. S. ( |
2014
Hartmann, I., Haspelmath, M., & Cysouw, M. (2014). Identifying semantic role clusters and alignment types via microrole coexpression tendencies. Studies in Language, 38(3), 463-484. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2014). Arguments and adjuncts as language-particular syntactic categories and as comparative concepts. Linguistic Discovery, 12(2), 3-11. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2014). Comparative syntax. In A. Carnie, Y. Sato, & D. Siddiqi ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2014). Descriptive hypothesis testing is distinct from comparative hypothesis testing: Commentary on Davis, Gillon, and Matthewson. Language, 90(4), e250-e257. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2014). On system pressure competing with economic motivation. In B. MacWhinney, A. L. Malchukov, & E. Moravcsik ( |
|
Haspelmath, M., Calude, A., Spagnol, M., Narrog, H., & Bamyaci, E. (2014). Coding causal–noncausal verb alternations: A form–frequency correspondence explanation. Journal of Linguistics, 50(3), 587-625. |
|
Michaelis, S., & Haspelmath, M.(2014). Ein Weltatlas der Kontaktsprachen. Retrieved from https://www.mpg.de/7770933/MPI_EVAN_JB_2014?c=8236817. |
2013
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Jezička promjena – poboljšanje ili kvarenje? Lingvazin: Magazin za jezik i književnost, 1(3), 20-22. Retrieved from http://www.izbjik.ba/index.php/publikacije/lingvazin#. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Alignment of case marking of full noun phrases. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Alignment of case marking of personal pronouns. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Co-occurrence of demonstrative and definite article. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Definite articles. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Dual in independent personal pronouns. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Expletive subject of existential verb. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Expression of nominal plural meaning. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Expression of pronominal subjects. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Functions of reduplication. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Indefinite articles. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Indefinite pronouns. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Independent pronominal possessors. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Intensifiers and reflexive pronouns. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Interrogative pronouns. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Marking of patient noun phrases. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Marking of possessor noun phrases. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Marking of pronominal possessors. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Negation and indefinite pronouns. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Nominal and verbal conjunction. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Occurrence of nominal plural markers. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Order of degree word and adjective. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Order of frequency adverb, verb, and object. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Order of recipient and theme in ditransitive constructions. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Paralinguistic usages of clicks. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Person syncretism in independent personal pronouns. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Politeness distinctions in second-person pronouns. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Position of definite article in the noun phrase. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Position of indefinite article in the noun phrase. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Position of interrogative phrases in content questions. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Position of standard negation. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Pronoun conjunction. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Reciprocal constructions. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Reflexive constructions. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Special dependent person forms for subject and object. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Michaelis, S. M. (2013). Aspect markers and inchoative meaning. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Michaelis, S. M. (2013). Ditransitive constructions with 'give'. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Michaelis, S. M. (2013). Focus particle 'also'. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Michaelis, S. M. (2013). Inclusive–exclusive distinction in independent personal pronouns. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Michaelis, S. M. (2013). Instrument relative clauses. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Michaelis, S. M. (2013). Negative morpheme types. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Michaelis, S. M. (2013). Order of cardinal numeral and noun. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Michaelis, S. M. (2013). Order of relative clause and noun. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Michaelis, S. M., & Haspelmath, M. (2013). Object relative clauses. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Michaelis, S. M., & Haspelmath, M. (2013). Subject relative clauses. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Michaelis, S. M., & Haspelmath, M. (2013). The associative plural. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Michaelis, S. M., & Haspelmath, M. (2013). Verb doubling in temporal clauses. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Michaelis, S. M., & Haspelmath, M. (2013). Vocative markers. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Michaelis, S. M., & Haspelmath, M. (2013). Want’ complement subjects. In S. M. Michaelis, P. Maurer, M. Haspelmath, & M. Huber ( |
|
Michaelis, S. M., Maurer, P., Haspelmath, M., & Huber, M. ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Why open-access publication should be nonprofit—a view from the field of theoretical language science. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 7: 57. |
|
Bakker, D., & Haspelmath, M. ( |
|
Dryer, M. S. (2013). The World Atlas of Language Structures Online. München: Max Planck Digital Library. Retrieved from http://wals.info/. |
|
Hartmann, I., Haspelmath, M., & Taylor, B. ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). Argument indexing: a conceptual framework for the syntax of bound person forms. In D. Bakker, & M. Haspelmath ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2013). On the cross-linguistic distribution of same-subject and different-subject 'want' complements: Economic vs. iconic motivation. SKY Journal of Linguistics, 26, 41-69. Retrieved from http://www.linguistics.fi/julkaisut/sky2013.shtml. |
|
Michaelis, S. M., Maurer, P., Haspelmath, M., & Huber, M. ( |
|
Michaelis, S., Maurer, P., Haspelmath, M., & Huber, M. ( |
|
Nordhoff, S., Hammarström, H., Forkel, R., & Haspelmath, M. ( |
2012
Haspelmath, M. (2012). Escaping ethnocentrism in the study of word-class universals. Theoretical Linguistics, 38(1-2), 91-102. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2012). How to compare major word-classes across the world's languages. In T. Graf, D. Paperno, A. Szabolcsi, & J. Tellings ( |
|
Tadmor, U., Haspelmath, M., & Taylor, B. (2012). Borrowability and the notion of basic vocabulary. In S. Wichmann, & A. P. Grant ( |
2011
Haspelmath, M. (2011). On S, A, P, T, and R as comparative concepts for alignment typology. Linguistic Typology, 15, 535-567. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2011). The gradual coalescence into "words" in grammaticalization. In H. Narrog ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2011). The indeterminacy of word segmentation and the nature of morphology and syntax. Folia Linguistica, 45(1), 31-80. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2011). The language system is abstract but cannot be understood without its social functions. Theoretical Linguistics, 37(1-2), 45-50. |
2010
Atoyebi, J., Haspelmath, M., & Malchukov, A. (2010). Ditransitive constructions in Yorùbá. In Andrej Malchukov; Martin Haspelmath; Bernard Comrie ( |
|
Comrie, B., Haspelmath, M., & Malchukov, A. L. (2010). Questionnaire on ditransitive constructions. In A. L. Malchukov, M. Haspelmath, & B. Comrie ( |
|
Cysouw, M., Haspelmath, M., & Malchukov, A. (2010). Introduction to the Special Issue "Semantic Maps: Methods and Applications". Semantic Maps: Methods and Applications, 1-3. |
|
Cysouw, M., Malchukov, A., & Haspelmath, M. ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2010). Comparative concepts and descriptive categories in crosslinguistic studies. Language, 86(3), 663-687. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2010). Framework-free grammatical theory. In Bernd Heine, Heiko Narrog ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2010). The Behaviour-before-Coding Principle in syntactic change. In Floricic, Franck ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2010). The interplay between comparative concepts and descriptive categories (Reply to Newmeyer). Language, 86(3), 696-699. |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Sims, A. D. (2010). Understanding morphology (2nd ed.). London: Hodder Education. |
|
Malchukov, A. L., Haspelmath, M., & Comrie, B. (2010). Studies in ditransitive constructions: a comparative handbook. Berlin: De Gruyter. |
|
Malchukov, A. L., Haspelmath, M., & Comrie, B. (2010). Ditransitive constructions: a typological overview. In Andrej Malchukov; Martin Haspelmath; Bernard Comrie ( |
|
Tadmor, U., Haspelmath, M., & Taylor, B. (2010). Borrowability and the notion of basic vocabulary. Diachronica, 27(2), 226-246. |
2009
Haspelmath, M. (2009). An empirical Test of the Agglutination Hypothesis. In Sergio Scalise; Elisabetta Magni; Antonietta Bisetto ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2009). Lexical borrowing: Concepts and issues. In ed. by Martin Haspelmath; Uri Tadmor ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2009). Terminology of Case. In Andrej Malchukov; Andrew Spencer ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2009). The best-supported language universals refer to scalar patterns deriving from processing cost. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 32(5), 457-458. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2009). The loanword typology project and the world loanword database. In Martin Haspelmath, Uri Tadmor ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2009). The typological database of the World Atlas of Language Structures. In Martin Everaert & Simon Musgrave ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2009). Welche Fragen können wir mit herkömmlichen Daten beantworten? Zeitschrift für Sprachwissenschaft, 28(1), 157-162. |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Tadmor, U. ( |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Tadmor, U. ( |
|
Haspelmath, M.(2009). Wörter mit Migrationshintergrund. Retrieved from https://www.mpg.de/385215/forschungsSchwerpunkt?c=166446. |
2008
Haspelmath, M. (2008). [Book Review]: Person, by Anna Siewierska. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press, 2004. Pp. xx, 327. ISBN 0521776694. Language, 84(1), 206-209. Retrieved from http://muse.jhu.edu/journals/language/v084/84.1haspelmath.pdf. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2008). A Frequentist Explanation of Some Universals of Reflexive Marking. Linguistic Discovery, 6(1), 40-63. Retrieved from http://journals.dartmouth.edu/cgi-bin/WebObjects/Journals.woa/2/xmlpage/1/document/633. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2008). Creating Economical Morphosyntactic Patterns in Language Change. In Jeff Good ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2008). Descriptive scales versus comparative scales. In Marc Richards & Andrej L. Malchukov ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2008). Ditransitive constructions: Towards a new Role and Reference Grammar account? In Robert D. Van Valin, Jr. ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2008). Frequency vs. iconicity in explaining grammatical asymmetries. Cognitive Linguistics, 19(1), 1-33. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2008). Loanword typology: Steps toward a systematic crosslinguistic study of lexical borrowability. In Thomas Stolz, Dik Bakker & Rosa Salas Palomo ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2008). Parametric versus functional explanations of syntactic universals. In Theresa Biberauer ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2008). Reply to Haiman and Croft. Cognitive Linguistics, 19(1), 59-66. |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Michaelis, S. (2008). Leipzig fourmille de typologues: Genitive objects in comparison. In Greville G. Corbett and Michael Noonan ( |
2007
Haspelmath, M. (2007). Coordination. In Shopen, Timothy ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2007). Ditransitive alignment splits and inverse alignment. Functions of Language, 14(1), 79-102. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2007). Further remarks on reciprocal constructions. In Vladimir P. Nedjalkov ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2007). Pre-established categories don't exist: Consequences for language description and typology. Linguistic Typology, 11(1), 119-132. |
2006
Haspelmath, M. (2006). [Book Review]: Preferred argument structure: Grammar as architecture for function. Ed. by JOHN W. DU BOIS, LORRAINE E. KUMPF, and WILLIAM J. ASHBY. (Studies in discourse and grammar 14.) Amsterdam: John Benjamins, 2003. ISBN 1588113698. $156 (Hb). Language, 82(4), 908-912. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2006). Against markedness (and what to replace it with). Journal of Linguistics, 42(1), 25-70. |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Siegmund, S. (2006). Simulating the replication of some of Greenberg's word order generalizations. Linguistic Typology, 10(1), 74-82. |
2005
Dryer, M. S. (2005). The World Atlas of Language Structures (M. Haspelmath, D. Gil, & B. Comrie, |
2004
Haspelmath, M. ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2004). Author´s response. Studies in Language, 28(3), 584-586. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2004). Coordinating constructions: an overview. In Haspelmath, Martin ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2004). Does linguistic explanation presuppose linguistic description? Studies in Language, 28(3), 554-579. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2004). Explaining the Ditransitive Person-Role Constraint: a usagebased account. Constructions, 2, 1-71. Retrieved from http://www.dipp.nrw.de/constructions/articles/35/DPRC0102-moddoulos.rtf.pdf. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2004). How hopeless is genealogical linguistics, and how advanced is areal linguistics? A review article of Aikhenvald, Alexandra Y. & Dixon, R.M.W. (ed.) 2001. Areal diffusion and genetic inheritance. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Studies in Language, 28(1), 209-223. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2004). On directionality in language change with particular reference to grammaticalization. In Olga Fischer, Muriel Norde and Harry Perridon ( |
2003
Michaelis, S., & Haspelmath, M. (2003). Ditransitive constructions: creole languages in a cross-linguistic perspective. Creolica. Retrieved from http://www.creolica.net/. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2003). Book Notice of: Sinha, Jasmin. 2000. Der neuostaramäische Dialekt von Bespen (Provinz Mardin, Südosttürkei): Eine grammatische Darstellung. Studies in Language, 27(3), 714-715. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2003). The geometry of grammatical meaning: Semantic maps and cross-linguistic comparison. New Psychology of Language, 2, 211-242. |
2002
Haspelmath, M. (2002). Understanding morphology. London: Arnold. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2002). Grammatikalisierung: von der Performanz zur Kompetenz ohne angeborene Grammatik. In Krämer, Sybille; König, Ekkehard ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2002). On understanding word order asymmetries: Comments on John A. Hawkins "Symmetries and asymmetries: their grammar, typology and parsing". Theoretical Linguistics, 28, 159-170. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2002). Warum ist Grammatik so, wie sie ist? In Müller, Horst M. ( |
2001
Comrie, B., & Haspelmath, M. (2001). Die Bibliothek von Babel. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2001). Non-canonical marking of core arguments in European languages. In A. Y. Aikhenvald, R. M. W. Dixon, & M. Onishi ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2001). The European linguistic area: Standard Average European. In Martin Haspelmath ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2001). Word classes/parts of speech. In P. B. Baltes, & N. J. Smelser ( |
|
Haspelmath, M., König, E., Oesterreicher, W., & Raible, W. (2001). Language typology and language universals: An international handbook. Berlin: de Gruyter. |
2000
Haspelmath, M. (2000). Converb. In K. Brown, & J. Miller ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2000). Optimality and diachronic adaptation. Zeitschrift für Sprachwissenschaft, 18, 180-205. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2000). Periphrasis, symphrasis, and morphosyntactic blocking. In V. J. Gusev ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2000). Periphrasis. In G. E. Booij, C. Lehmann, & J. Mugdan ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2000). Some issues concerning optimality and diachronic adaptation (author's response to open peer commentary). Zeitschrift für Sprachwissenschaft, 18, 251-68. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2000). The relevance of extravagance: A reply to Bart Geurts. Linguistics, 38, 789-98. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2000). Why is grammaticalization irreversible? Linguistics, 37, 1043-68. |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Caruana, S. (2000). Subject diffuseness in Maltese: On some subject properties of experiential verbs. Folia Linguistica, 34(3-4), 245-265. |
1999
Haspelmath, M. (1999). Explaining article-possessor complementarity: economic motivation in noun phrase syntax. Language, 75, 227-43. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (1999). External possession in a European areal perspective. In D. L. Payne, & I. Barshi ( |
|
Haspelmath, M. (1999). Long distance agreement in Godoberi (Daghestanian) complement clauses. Folia Linguistica, 33, 131-151. |
|
Haspelmath, M., & König, E. (1999). Der europäische Sprachbund - ein Schritt in die Zukunft. In N. Reiter ( |
1998
Haspelmath, M. (1998). Does grammaticalization need reanalysis? Studies in Language, 22, 49-85. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (1998). How young is Standard Average European? Language Sciences, 20, 271-287. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (1998). The semantic development of old presents: New futures and subjunctives without grammaticalization. Diachronica, 15, 29-62. |
|
Haspelmath, M., & Buchholz, O. (1998). Equative and similative constructions in the languages of Europe. In J. v. d. Auwera ( |
|
Haspelmath, M., & König, E. (1998). Concessive conditionals in the languages of Europe. In J. v. d. Auwera ( |
2021
Haspelmath, M. (2021). Explaining diverse language structures from convergent evolution of linguistic conventions. Talk presented at Birmingham Lectures. Birmingham. 2021-03-09. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2021). From community competition to complementarity in general linguistics: The eight complementary why questions. Talk presented at XIV Congreso Internacional de Lingüística General. Sevilla. 2021-06-23. |
|
Haspelmath, M. (2021). Structural, evolutionary and biocognitive explanations are mutually compatible. Talk presented at Center of Linguistic Sciences of Beijing Normal University. Beijing. 2021-04-30. |
 Open Access
Open Access